What is Distributed Operating System | Distributed OS |Architecture and Types of Distributed Operating system
What is Distributed Operating System ?
- Distributed operating system is one kind of model where distributed applications are running on different multiple computers which are linked by communication network .
- Distributed OS is an extension of network operating system which supports higher level of communication and integration of different mechines or computers connected on that network .
- The Distributed OS involves a collection of autonomous computer system that are capable of communicating and co-operating with each other via LAN / WAN .It provides users to share mechine resources throughout that network .
- Don't be confused that the system connected in a distributed network have their own memory and OS or not . In Distributes OS each computers present on that network has their own memory and runs it's own operating system .
- A Distributed system may consists of multiple computers that do not share their memory .
- The communication among the computers of a distributed system is done by message sharing over a communication network .
Advantages of Distributed operating System :
- Sharing of resources
- Reliability
- Communication around the network
- Computation and workflow speedup.
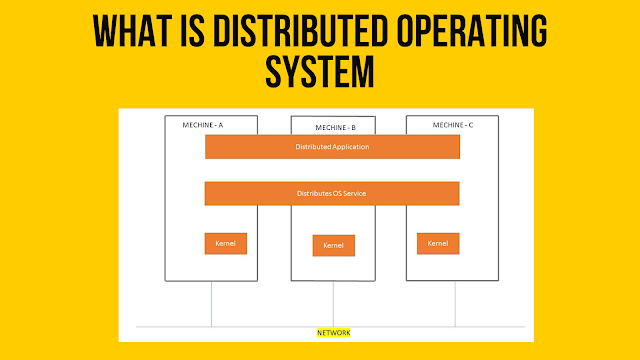
Architechture of Distributed OS :
- In Distributed Operating System hardware and software components are located at remote networked computers co-ordinate and communicate their actions only through message sharing .Any distance among the computers may separeate computers in the network .
- The main motive of making Distributed OS is the sharing of resources . In distributed system there might be many cases like resources may be managed by the servers and accessed by the clients .
- A Distributed System basically runs on multiple computers connected with each other through a communication network but they appears like a single system .
Difference between Message passing and Shared Memory :
Message Passing :
- In message passing communication takes place by the exchange of message between the co-operating System .
- It does not run processes concurrently .
- It become easier for implementing interprocess communication .
- It looses the coupling of program components.
- Explicit communication via messages . E.G : Telephone call .
Shared Memory :
- In this process memory is shared by co-operating process which can eaxchange information by adding a timestamp of reading date and writting date .
- It helps in running processes concurrently.
- It is not easier for implementing interprocess communication.
- It provides tight coupling .
- It provide implicit communication via memory operation . E.g , Bukketin Board .
Thank you for reading this article -:)